Types of Home Loans: Which is Right for You?

When it comes to purchasing a home, one of the most crucial decisions you’ll make is choosing the right home loan. With a myriad of mortgage products available, navigating through the options can feel overwhelming. Understanding the different types of home loans, their terms, and their implications can empower you to make an informed choice that aligns with your financial goals.
Mortgage Basics: Terms and Rates
Before diving into specific mortgage types, it’s essential to grasp some foundational concepts regarding how mortgages operate. The term of a mortgage refers to the duration over which you will repay the loan. Common terms include 15-year and 30-year mortgages. A 15-year mortgage divides your payments into 180 equal installments, while a 30-year mortgage spreads payments over 360 installments.
Interest rates can significantly impact your monthly payment and overall financial commitment. They can be classified as either fixed-rate or adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs). Fixed-rate mortgages maintain the same interest rate throughout the life of the loan, providing predictability in monthly payments. Conversely, ARMs feature an interest rate that fluctuates based on market conditions, which can lead to varying monthly payments.
Exploring Different Types of Mortgages
Fixed-Rate Mortgages
A fixed-rate mortgage is often the most straightforward option for borrowers seeking stability. With this type of mortgage, your interest rate remains constant throughout the entire term of the loan—whether it’s 15 or 30 years. This predictability makes budgeting easier, as you’ll know exactly what your monthly payment will be until the loan is paid off. For many homeowners who plan on staying in their homes long-term, this type of mortgage is appealing due to its consistency and security against rising interest rates.
Adjustable-Rate Mortgages (ARMs)
On the other hand, adjustable-rate mortgages offer lower initial rates that can be enticing for first-time buyers or those looking to minimize upfront costs. For instance, a 7/1 ARM features a fixed rate for the first seven years, after which it adjusts annually based on market indices. While ARMs can provide savings initially, they carry inherent risks; if market rates rise significantly after your initial fixed period ends, your monthly payments could increase substantially.
Specialty Loan Programs
In addition to traditional fixed and adjustable-rate mortgages, there are specialty loan programs designed for specific borrower needs:
- FHA Loans: Backed by the Federal Housing Administration (FHA), these loans are ideal for first-time homebuyers or those with lower credit scores as they require smaller down payments—often as low as 3.5%.
- VA Loans: Available to eligible veterans and active-duty service members, VA loans offer competitive rates without requiring a down payment or private mortgage insurance (PMI).
- USDA Loans: For those looking to buy in rural areas, USDA loans provide financing with no down payment required for qualifying low- to moderate-income applicants.
Making Your Decision
Choosing the right mortgage involves evaluating not only your current financial situation but also your future plans. Consider factors such as how long you plan to stay in your home, your tolerance for risk regarding fluctuating rates, and whether you qualify for specialty programs that could save you money.
Before finalizing any decision, take time to compare various lenders and their offerings. Mortgage rates can vary significantly between institutions; securing a favorable rate could save you thousands over the life of your loan.
Conventional Mortgages
When it comes to securing a home loan, conventional mortgages often emerge as the most prevalent option available to borrowers. These loans, primarily offered through government-sponsored enterprises (GSEs) like Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, provide a traditional pathway for financing residential properties. Unlike government-backed mortgages such as those insured by the Federal Housing Administration (FHA), conventional mortgages come with distinct characteristics that cater to a specific segment of homebuyers.
Who Are Conventional Mortgages Best For?
Conventional mortgages are ideally designed for well-qualified buyers who have strong financial profiles and do not belong to specific demographic groups eligible for government-backed financing. This includes first-time homebuyers with good credit histories, as well as repeat buyers looking to purchase primary residences or investment properties. If you possess a stable income, a reliable credit score, and can meet the necessary financial thresholds, a conventional mortgage could be an excellent choice for your home financing needs.
Requirements for Conventional Mortgages
Before diving into the benefits and drawbacks of conventional mortgages, it is essential to understand their basic requirements:
- Credit Score: A minimum credit score of 620 is typically required to qualify for a conventional mortgage. The higher your credit score, the better your chances of securing favorable loan terms.
- Down Payment: Borrowers must provide at least 3% of the home’s purchase price as a down payment. However, if your down payment is less than 20%, private mortgage insurance (PMI) will be necessary.
- Income Verification: Lenders usually require verifiable income documentation spanning at least two years to ensure that borrowers can manage their mortgage payments.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI): A DTI ratio of 43% or less is typically expected. This ratio assesses your monthly debt payments against your gross monthly income to determine your borrowing capacity.
Pros and Cons of Conventional Mortgages
Like any financial product, conventional mortgages come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages that potential borrowers should consider before making a decision.
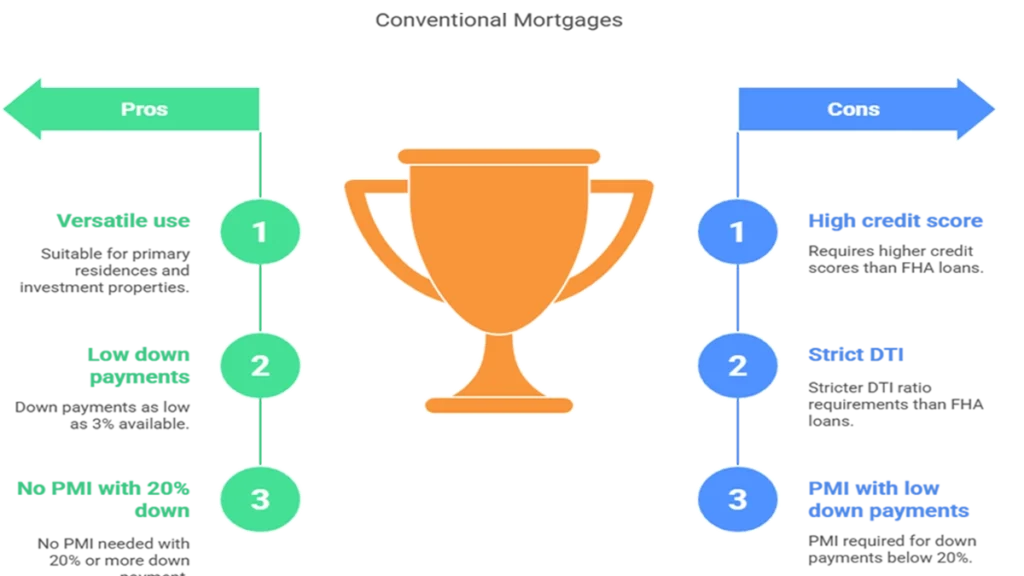
Pros
- Versatility: Conventional mortgages can be used not only for purchasing primary residences but also for financing investment properties.
- Low Down Payments: With down payments starting as low as 3%, these loans can be accessible even for those who may not have significant savings.
- Elimination of PMI: If you can afford a down payment of 20% or more, you can avoid the additional cost of private mortgage insurance altogether.
Cons
- Higher Credit Score Requirements: Compared to FHA loans, which are more lenient with credit scores, conventional mortgages demand stronger credit histories from borrowers.
- Stricter DTI Ratio Standards: The maximum allowable DTI ratio is more stringent with conventional loans than it is with FHA options.
- PMI Costs on Lower Down Payments: While PMI can be avoided with larger down payments, those putting less than 20% down will incur extra monthly costs until they reach sufficient equity in their homes.
Government-Backed Mortgage Programs
Fortunately, the U.S. government has established several mortgage programs designed to facilitate homeownership, particularly for individuals in rural areas, low-income neighborhoods, and veterans. Among these, USDA loans stand out as an exceptional choice for those seeking affordable home financing without the burden of a hefty down payment.
Spotlight on USDA Loans
The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) loan program is specifically designed to promote homeownership in rural areas that may lack significant development. This program provides an attractive option for eligible borrowers due to its unique features—most notably, it allows qualified individuals to secure a mortgage with no down payment and without the need for PMI.
Requirements for USDA Loans
While USDA loans offer compelling benefits, there are specific eligibility criteria that potential borrowers must meet:
- Location: The property must be situated in an area designated as rural by the USDA.
- Income Limits: Borrowers’ household income must fall within specified limits set by the USDA.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio: Generally, borrowers should maintain a debt-to-income (DTI) ratio of 41% or lower; however, there are exceptions based on other compensating factors.
- Credit Score: A minimum credit score of 620 is typically required, though exceptions may apply.
Pros and Cons of USDA Loans
As with any financial product, USDA loans come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages that potential borrowers should consider before proceeding.
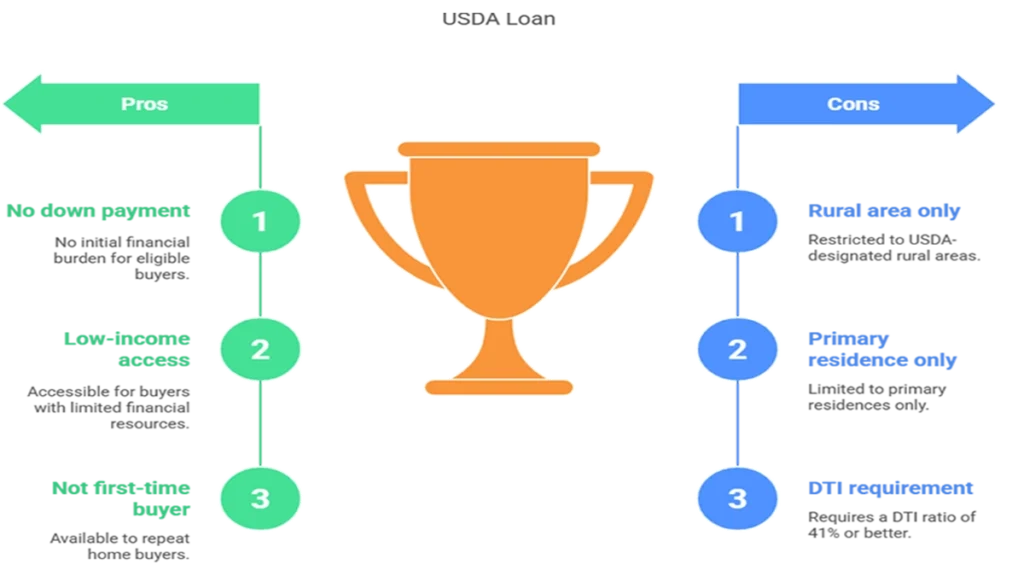
Pros:
- No Down Payment Required: One of the most appealing aspects is that eligible borrowers can finance 100% of their home purchase price.
- Accessible to Low- and Moderate-Income Buyers: The program is specifically tailored to support those who may not have substantial savings.
- Not Limited to First-Time Homebuyers: Unlike some programs that restrict assistance to first-time buyers, USDA loans are available for repeat purchasers as well.
Cons:
- Property Location Restrictions: The requirement that properties must be located in a USDA-designated rural area can limit options for some buyers.
- Primary Residence Requirement: USDA loans can only be used for homes intended as primary residences, excluding investment properties.
- DTI Ratio Constraints: Borrowers must maintain a DTI ratio of 41% or better unless qualifying exceptions apply.
FHA Loans
FHA loans are mortgages that are insured by the Federal Housing Administration but issued by any FHA-approved lender. Unlike HUD loans, which cater to specific circumstances such as Section 184 for Native Americans, FHA loans are designed to assist low-income borrowers in purchasing homes. They offer more flexible income and credit score requirements compared to conventional mortgages, making them an attractive option for many.
As of 2024, it’s essential to note that while FHA loans provide easier access to homeownership, they come with certain costs. Borrowers are required to pay an upfront mortgage insurance premium equivalent to 1.75% of the loan amount, alongside annual mortgage insurance premiums throughout the life of the loan.
Who Are FHA Loans Best For?
FHA loans are particularly beneficial for individuals who may struggle to qualify for traditional home loans due to stringent credit and income requirements. If you find yourself in one of these situations—whether it’s a low credit score or a limited savings account—FHA loans can provide a pathway to homeownership that might otherwise be closed off.
Requirements for FHA Loans
To qualify for an FHA loan, potential borrowers must meet several key criteria:
- Credit Score: You can qualify with a credit score as low as 500 if you make a down payment of at least 10%. If your credit score is 580 or higher, you can secure an FHA loan with a down payment as low as 3.5%.
- Down Payment: The minimum down payment requirement is just 3.5%, making it significantly easier for buyers who may not have substantial savings.
- Income Verification: Borrowers must demonstrate verifiable income over the past two years.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI): Generally, your DTI ratio should not exceed 43% to ensure that you can comfortably manage your mortgage payments alongside other debts.
Pros and Cons of FHA Loans
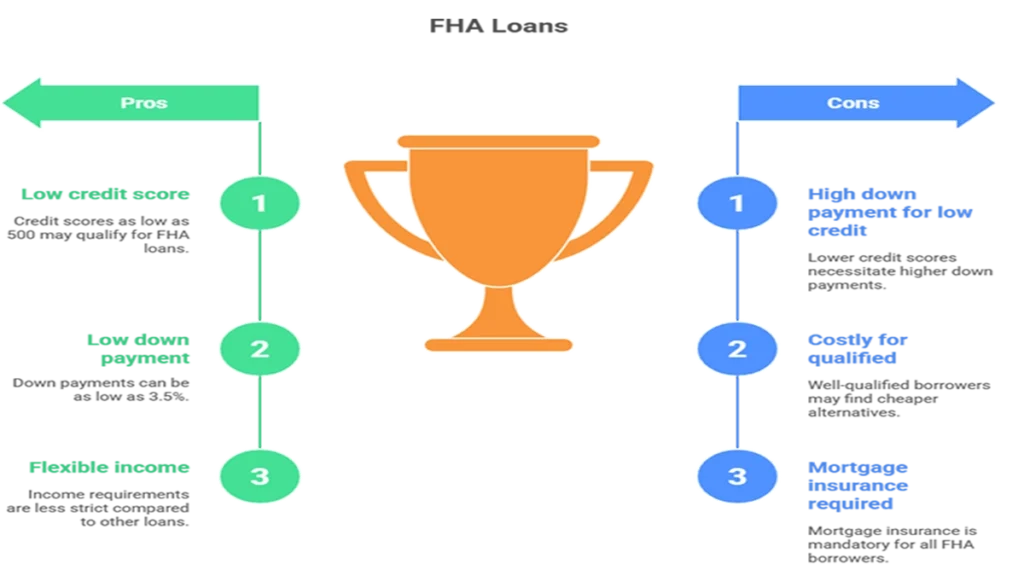
Pros
- Flexible Credit Requirements: With credit score requirements starting at just 500, FHA loans provide opportunities for borrowers who might not qualify elsewhere.
- Low Down Payment: The ability to put down only 3.5% allows many first-time homebuyers access to the housing market without needing significant savings.
- Less Stringent Income Requirements: This flexibility makes it easier for those with irregular income streams or lower earnings to secure financing.
Cons
- Higher Down Payments for Low Credit Scores: While some borrowers can qualify with lower scores, they must still contend with higher down payments.
- Potentially Higher Overall Costs: For well-qualified borrowers who have good credit scores and financial histories, other mortgage options may be cheaper in terms of interest rates and fees over time.
- Mandatory Mortgage Insurance: All borrowers must pay mortgage insurance premiums regardless of their credit score or down payment amount.
VA Loans
In the realm of home financing, U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) loans stand out as a powerful resource tailored specifically for veterans and active military personnel. These loans, backed by the VA and issued by approved lenders, offer unique advantages that can make the dream of homeownership a reality for many who have served our country.
VA loans are government-backed mortgage options designed to assist veterans, active-duty service members, and certain members of the National Guard and Reserves in purchasing homes. Similar to Federal Housing Administration (FHA) loans, these loans are issued according to specific guidelines set forth by the VA, making them an attractive alternative to conventional mortgages. Notably, VA loans share some features with USDA loans, including no down payment requirement and no mortgage insurance—making them financially appealing for eligible borrowers.
Eligibility Requirements
To access the benefits of a VA loan, borrowers must meet certain eligibility criteria:
- Certificate of Eligibility (COE): Borrowers must obtain a COE from the VA to demonstrate their eligibility based on service length or circumstances.
- Credit Score: While the VA does not impose a minimum credit score requirement, most lenders prefer scores of 620 or higher.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI): A DTI ratio of 41% or less is generally recommended to ensure that borrowers can manage their mortgage payments alongside existing debts.
- Income Verification: Lenders typically require verifiable income for at least two years; however, exceptions may apply in certain situations.
- Primary Residence: VA loans can only be used for primary residences with limited exceptions for investment properties or second homes.
Pros and Cons of VA Loans
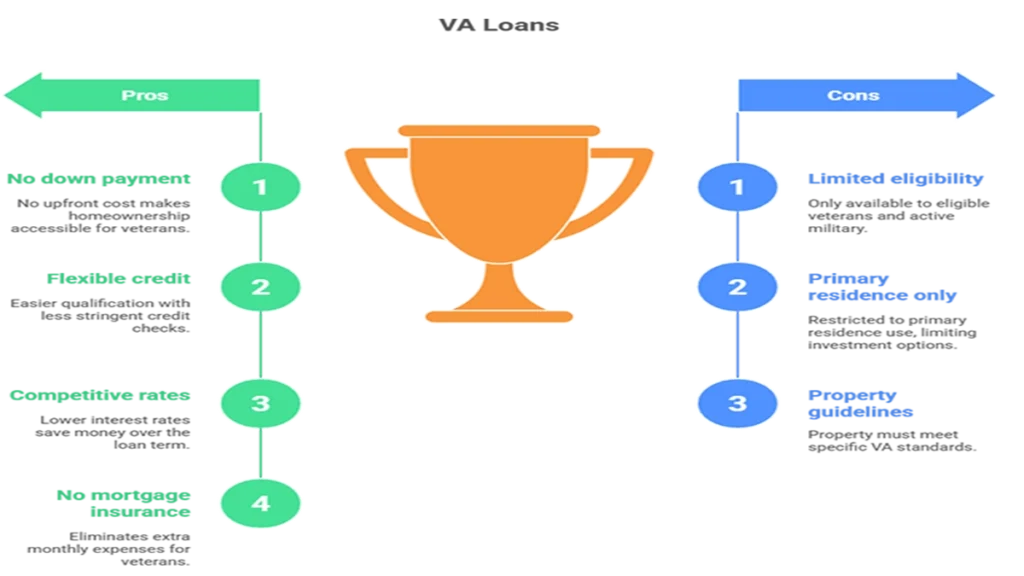
Pros
- No Down Payment Required: One of the most significant advantages is that eligible borrowers can finance 100% of the home’s value without needing a down payment.
- Flexible Credit Requirements: With more lenient credit requirements than conventional mortgages, VA loans provide opportunities for those who might struggle with traditional financing options.
- Competitive Interest Rates: Because they are backed by the government, VA loans often feature lower interest rates compared to other loan types.
- No Mortgage Insurance: Unlike FHA or conventional loans that typically require private mortgage insurance (PMI), VA loans do not carry this additional cost, further enhancing affordability.
Cons
- Eligibility Restrictions: Only veterans and active military personnel who meet specific service requirements can qualify for a VA loan.
- Usage Limitations: These loans are restricted to primary residences; therefore, they cannot be used for vacation homes or investment properties without meeting stringent guidelines.
- Property Requirements: To qualify for a VA loan, properties must meet specific standards set by the VA to ensure safety and livability.
Conclusion
Selecting the right home loan is not merely about finding the lowest interest rate; it’s about understanding how different types of mortgages align with your financial goals and lifestyle preferences. Whether you opt for a stable fixed-rate mortgage or consider an ARM with its tempting initial rates—or even explore specialty loan options—being well-informed will help ensure that you make a choice that supports your journey toward homeownership.
Conventional mortgages represent a solid option for well-qualified buyers seeking financing without the backing of government agencies. They offer flexibility in property types and allow for relatively low down payments; however, they also come with stricter requirements regarding credit scores and debt-to-income ratios compared to other loan types like FHA loans. Best regards, Finance Mate Club





